Mybatis Plus 学习
框架搭建
引入MybatisPlus的依赖
MybatisPlus官方提供了starter,其中集成了Mybatis和MybatisPlus中的所有功能,并且实现了自动装配效果,因此我们可以用MyBatisPlus的starter代替Mybatis的starter
<!-- MyBatis-Plus 核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>定义Mapper
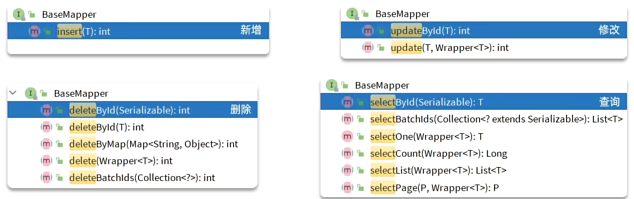
自定义的Mapper继承MybatisPlus提供的BaseMapper接口:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User>{
}
常见的注解
MybatisPlus通过扫描实体类,并基于反射获取实体类信息作为数据库表信息

@TableName:用来指定表名
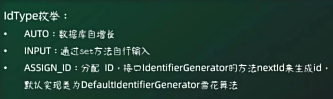
@TableId:用来指定表中的主键字段信息。
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;@TableField:用来指定表中的普通字段信息。
使用场景:
- 成员变量与数据库字段名不一致
- 成员变量名以is开头,且是布尔值
- 成员变量与数据库关键字冲突
- 成员变量不是数据库字段 举例:@TableField(exist = false)
条件构造器
MybatisPlus支持各种复杂的where条件,可以满足日常开发的所有需求

Wrapper 体系介绍
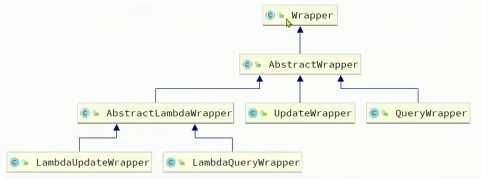
- Wrapper:条件构造抽象类,最顶端父类
- AbstractWrapper:用于查询条件封装,生成sql的where条件
- QueryWrapper:查询条件封装
- UpdateWrapper:update条件封装
- AbstractLambdaWrapper:使用Lambda语法
- LambdaQueryWrapper:用于Lambda语法使用的查询Wrapper
- LambdaUpdateWrapper:用于Lambda语法更新Wrapper
- AbstractWrapper:用于查询条件封装,生成sql的where条件
构造器常用方法
| 函数名 | 说明 | 说明/例子 |
|---|---|---|
| eq | 等于= | 例:eq(“name”,“zhangsan”) —> name = ‘zhangsan’ |
| ne | 不等于<> | 例:ne(“name”,“zhangsan”) —> name <> ‘zhangsan’ |
| gt | 大于> | 例:gt(“age”,18) —> age > 18 |
| ge | 大于等于>= | 例:ge(“age”,18) —> age >= 18 |
| lt | 小于< | 例:lt(“age”,18) —> age < 18 |
| le | 小于等于<= | 例:le(“age”,18) —> age <= 18 |
| between | between 值1 and 值2 | 例:between(“age”,10,20) —> age between 10 and 20 |
| notBetween | not between 值1 and 值2 | 例:notBetween(“age”,10,20) —> age not between 10 and 20 |
| like | like ‘%值%’ | 例:like(“name”,“强”) —> name like ‘%强%’ |
| notLike | not like ‘%值%’ | 例:notLike(“name”,“强”) —> name not like ‘%强%’ |
| likeLeft | like ‘%值’ | 例:likeLeft(“name”,“飞”) —> name like ‘%强’ |
| likeRight | like ‘值%’ | 例:likeRight(“age”,18) —> age <= 18 |
| isNull | 字段 is null | 例:isNull(“emal”) —> email is null |
| isNotNull | 字段 is not null | 例:isNotNull(“emal”) —> email is not null |
| in | 字段 in (值1,值2…) | 例:in(“age”,{10,18,30}) —> age in (10,18,30) |
| notIn | 字段 not in (值1,值2…) | 例:notIn(“age”,{10,18,30}) —> age not in (10,18,30) |
| inSql | 字段 in ( sql语句 ) | inSql(“id”, “select id from table where name like ‘%J%’”)—> id in (select id from table where name like ‘%J%’) |
| notInSql | 字段 not in ( sql语句 ) | notInSql(“id”, “select id from table where name like ‘%J%’”)—> id not in (select id from table where name like ‘%J%’) |
| orderBy | 排序 ordery by 字段,… | 例:orderBy(true,true,“id”,“name”) —> order by id asc,name asc |
| orderByDesc | 降排序 order by 字段,… desc | 例:orderByDesc(“id”,“name”) —> order by id desc,name desc |
| having | having (sql语句) | having(“sum(age) > {0}”,18) —> having sum(age) > 18 |
| or | 拼接or | 例:eq(“id”,1).or().eq(“name”,“老王”) —> id =1 or name = ‘老王’ |
| and | and 嵌套 | 例:and(i -> i.eq(“name”,“李白”).ne(“status”,“活着”))—> and (name = ’李白‘ and status <> ‘活着’) |
| exists | 拼接exists (sql语句) | 例:exists(“select id from table where age = 1”) |
| not exists | 拼接not exists (sql语句) | 例:not exists(“select id from table where age = 1”) |
举例
- QueryWrapper 使用
void testQueryWrapper(){
//构建查询条件
QueryWrapper<User> userQueryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>()
.select("id","username","info","balance")
.like("username","o")
.ge("balance",1000);
//查询
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(userQueryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}void testUpdateByQueryWrapper(){
//要更新的数据
User user = new User();
user.setBalance(2000);
//更新的条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>().eq("username", "jack");
//更新
userMapper.update(user, wrapper);
}- LambdaQueryWrapper 的使用
void testLambdaQueryWrapper(){
//构建查询条件
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<User>()
.select(User::getId,User::getUsername,User::getInfo,User::getBalance)
.like(User::getUsername,"o")
.ge(User::getBalance,1000);
//查询
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(lambdaQueryWrapper);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}自定义SQL
我们可以利用MyBatisPlus的Wrapper来构建复杂的where条件,然后自己定义SQL语句中剩下的部分。
为什么需要自定义SQL
我们的方法是在Service层实现,一些复杂的数据库操作(除where条件部分外的操作,比如set)在方法中需要用SQL语句来实现,但是在实际开发中,SQL语句需要在mapper中实现,这样不符合开发规范
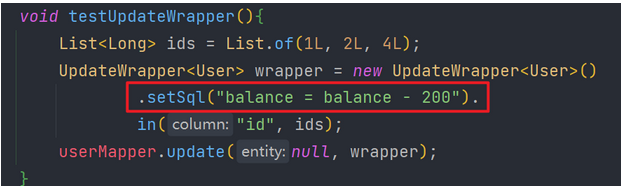
解决方案:我们可以利用MyBatisPlus的Wrapper来构建复杂的where条件,然后自己定义SQL语句中剩下的部分
- 首先,基于Wrapper构建where条件
void testCustomSqlUpdate(){
//更新条件
List<Long> ids = List.of(1L, 2L, 4L);
int amount = 200;
//定义条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>().in("id", ids);
//调用自定义SQL方法
userMapper.updateBalanceByIds(wrapper, amount);
}- 然后,在mapper方法参数中用Param注解声明wrapper变量名称,必须是 ew
void updateBalanceByIds(@Param("ew") QueryWrapper<User> wrapper, @Param("amount") int amount);- 最后,自定义SQL,并使用Wrapper条件
<update id="updateBalanceByIds">
update user
set balance = balance - #{amount} ${ew.customSqlSegment}
</update>Service接口
MybatisPlus不仅提供了BaseMapper,还提供了通用的Service接口及默认实现,封装了一些常用的service模板方法
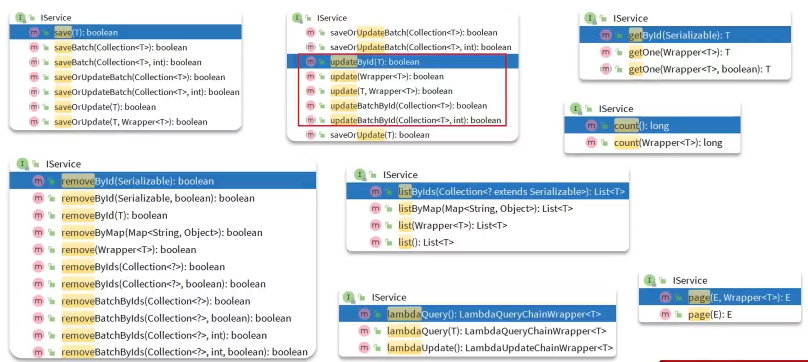
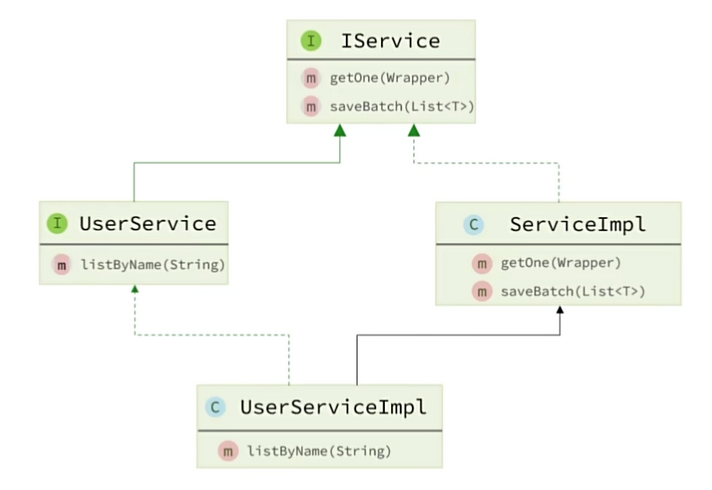
使用流程
- 自定义Service 接口继承IService接口
public interface IUserService extends IService<User>{
}- 自定义Service实现类,实现自定义接口并继承ServiceImpl
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements IUserService {
}IService的Lambda查询
上面在进行复杂条件查询时,是通过Wrapper条件构造器和自定义sql来实现的,还可以使用Iservice中的Lambda方法进一步优化代码
- 使用lambdaQuery查询
@Override
public List<User> queryUsers(String name, Integer status, Integer minBalance, Integer maxBalance){
return lambdaQuery()
.like(name != null, User::getUserName, name)
.eq(status != null, User::getStatus, status)
.ge(minBalance != null, User::getMinBalance, minBalance)
.le(maxBalance != null, User::getMaxBalance, maxBalance)
.list(); // .one():最多1个结果 .list():返回集合结果 .count():返回计数结果
}或者这种格式(引用别的Mapper)
List<Client> clientList = clientMapper.selectList(Wrappers.<ClientModel>lambdaQuery()
.eq(status != null, User::getStatus, status)
.ge(minBalance != null, User::getMinBalance, minBalance)
.le(maxBalance != null, User::getMaxBalance, maxBalance));- 使用lambdaQuery更新
@Override
@Transactional
public void deductBalance(Long id, Integer money){
User user = getById(id);
int remainBalance = user.getBalance() - money;
lambdaUpdate()
.set(User::getBalance, remainBalance)
.set(remainBalance == 0, User::getStatus, 2)
.eq(User::getId, id)
.eq(User::getBalance, user.getBalance()) // 乐观锁
.update();
}IService 批量更新
需求:批量插入10万条用户数据,并作出对比
- 普通的for循环插入
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++) {
userService.save(buildUser(i)); // buildUser为自定义构建User对象的方法
}普通的for循环逐条插入速度极差,不推荐
- MP的批量新增
// 每次批量插入1000条数据,插入100次即10万条数据
// 1、准备一个容量为1000的集合
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
//2、添加一个User
list.add(buildUser); // buildUser为自定义构建User对象的方法
//3、每1000条批量插入一次
if (i % 1000 == 0) {
userService.saveBatch(list);
// 4、清空集合,准备下一条数据
list.clear();
}
}MP的批量新增,机遇预编译的批处理,性能不错;与数据库建立的连接数会大幅减少,但是执行新增sql是一条一条执行,所有性能有待提升
- 开启 rewriteBatchedStatements=true 配置(性能最好)
开启该配置的效果为
INSERT INTO question (exam_id, content) VALUES (?, ?), (?, ?), (?, ?);枚举处理器
User 类中有一个用户状态字段需要设置为枚举类型,但是数据库中存储该字段为int类型,如何将用户类中的枚举类型和数据库中的字段对应上?
- 使用@EnumValue注解,将该字段与数据库中字段对应上;当后端需要返回数据给前端时,由于类中存在枚举类,所以默认返回的是枚举类的名称,如果需要自定返回枚举类中对应的code字段值或者是value的值,可以使用@JsonValue 注解实现
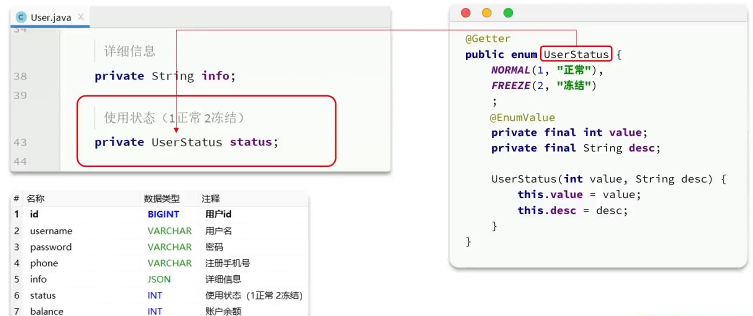
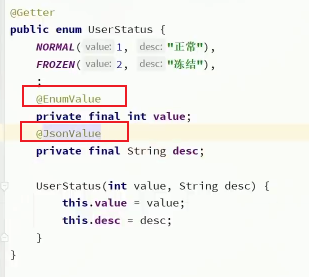
- 在application.yml中配置全局枚举处理器

Json 处理器
和上面的处理器类似,就是用来处理Json转换的处理器
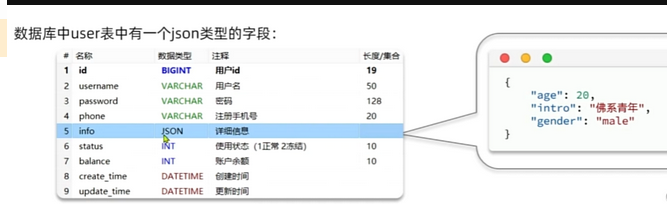
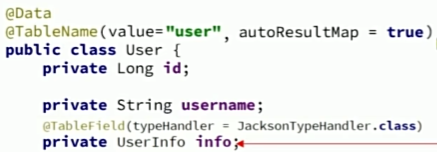
我们要将user表中的JSON格式转换成对象

但是mybatis不能自动将对象和json数据进行转换 我们要在要进行转换的元素加入注解@TableField,这个处理器mp没有提供在application文件配置的方法,多个元素要分别加上这个注解,而且如图所示也出现了对象的嵌套,我们就要定义复杂的resultMap,如果我们不想定义resultMap就要在类上加入@TabelName注解;就可以帮我们实现对象和json数据的转换了
插件功能
分页插件
首先,要在配置类中注册MyBatisPlus的核心插件,同时添加分页插件
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//1,创建分页插件
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL);
//设置查询最大上限
paginationInnerInterceptor.setMaxLimit(1000L);
//2.添加分页插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor);
return interceptor;
}
}接着,就可以使用分页的API了
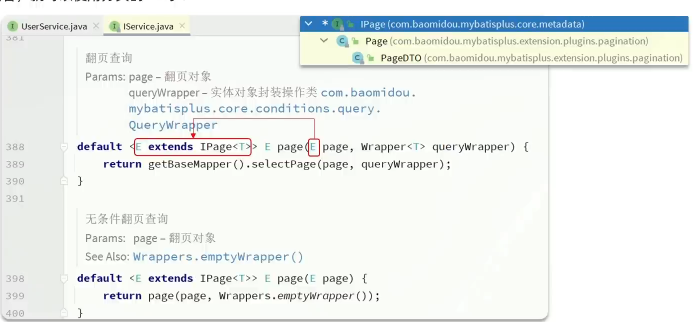
实例
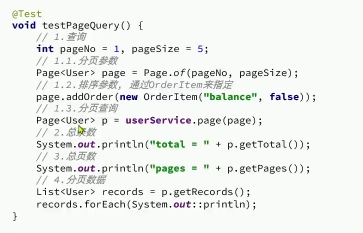
通用分页实体
- 创建分页实体类
@ApiModel(description = "页码查询条件实体")
@Data
public class pageQuery {
@ApiModelProperty("页码")
private Integer pageNo;
@ApiModelProperty("页数")
private Integer pageSize;
@ApiModelProperty("排序字段")
private Integer pageBy;
@ApiModelProperty("是否升序")
private Integer isAsc;
}- 需要分页的实体类继承分页实体类

- 创建一个分页结果实体类,是dto类型,这里的dto是返回给前端数据封装的实体类

- 查询实例
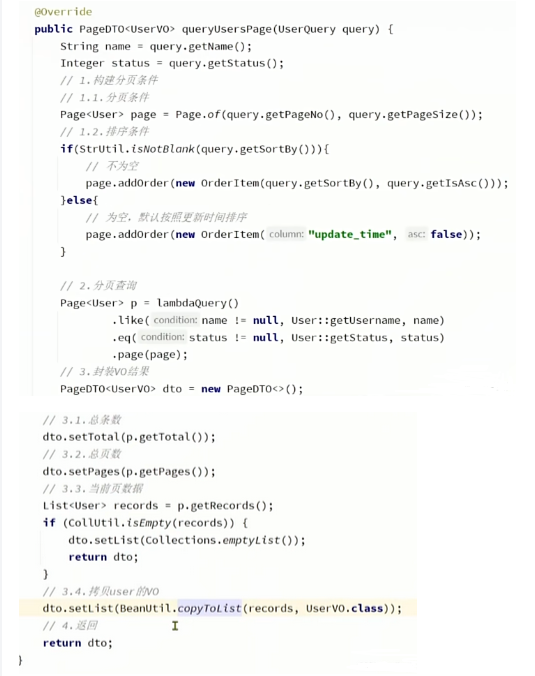
总结使用流程图

